Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology encompasses the diagnosis and treatment of all eye diseases, including medical and surgical interventions. It involves understanding the intricate structures of the eye and their functions.
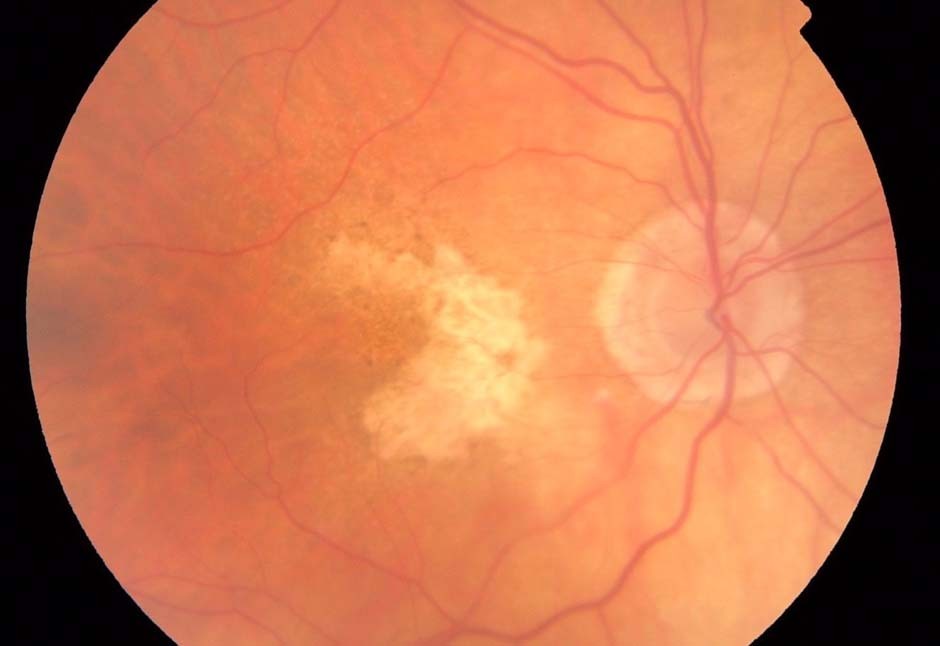
Geographic Atrophy
Geographic Atrophy ACRP-certified professionals ensuring smooth trial execution.
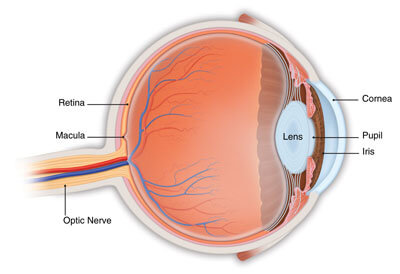
Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Macular Degeneration (AMD) Personalized strategies to enroll and retain diverse patient populations.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy E-source data capture, EMR integration, and real-time tracking for seamless research.

Macular Edema
Macular Edema HIPAA-compliant security, 21 CFR Part 11-compliant EHR, and encrypted databases for PHI protection.
Retina vein Occlusion (RVO)
Retina vein Occlusion (RVO) HIPAA-compliant security, 21 CFR Part 11-compliant EHR, and encrypted databases for PHI protection.
Glaucoma
GlaucomaHIPAA-compliant security, 21 CFR Part 11-compliant EHR, and encrypted databases for PHI protection.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-c-diff-overview-7485174-final-10895d4d8a804ac78b5ceaaaaacf516e.png)